The electromagnetic spectrum is the name for the different forms of light that are given off by objects in the Universe.
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays are all types of light, but with different energies!
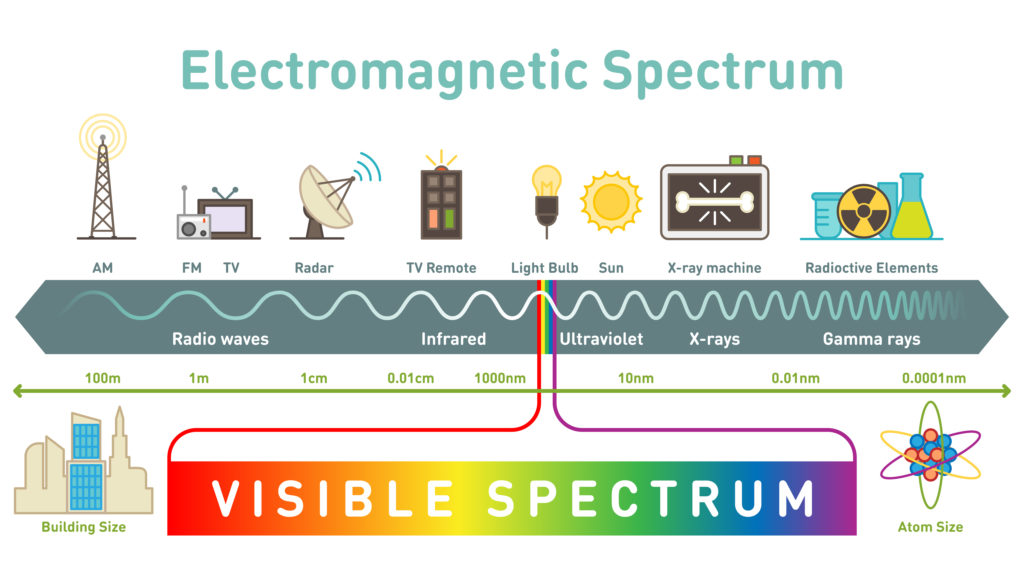
The different types of light have different wavelengths.
What is wavelength?
Wavelength is the length of one wave. The longer the wavelength the less energy the waves have.
Radio waves have a wavelength that is a similar size to a building, while x rays have a wavelength the size of an atom! That’s a big difference!
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength and the most energy. They are also the most ionising.
Where do the different types of light in the electromagnetic spectrum come from?
Gamma rays and x-rays – these can come from natural sources such as radioactive elements but can also be man made.
Ultraviolet radiation – the Sun
Visible light – the Sun, lightbulbs
Infrared radiation – the Sun, people
Microwaves – microwaves occur naturally but can also be man-made like those used in microwave ovens.
Radio waves – radio waves are produced when an alternating current flows in an aerial.
Where is electromagnetic radiation used?
Where are gamma rays used?
Gamma rays kill microbes so can be used for sterilisation of objects and food. They are also used for cancer treatments and for medical imaging.
Where are x-rays used?
X-rays are used to view inside objects and materials. You’ve probably seen an x-ray scanner at an airport that looks for metal objects and if you’ve ever broken a bone, you may have had an x-ray. X-rays are transmitted by skin but absorbed by denser materials such as bone.
Where is infrared radiation used?
Infrared radiation is used in heaters and infrared cameras for thermal imaging.
Infrared can be used to transfer information between electronic devices and is used in TV remote controls.
Where is UV light used?
UV light is used in fluorescent lights and sometimes for sterilising water.
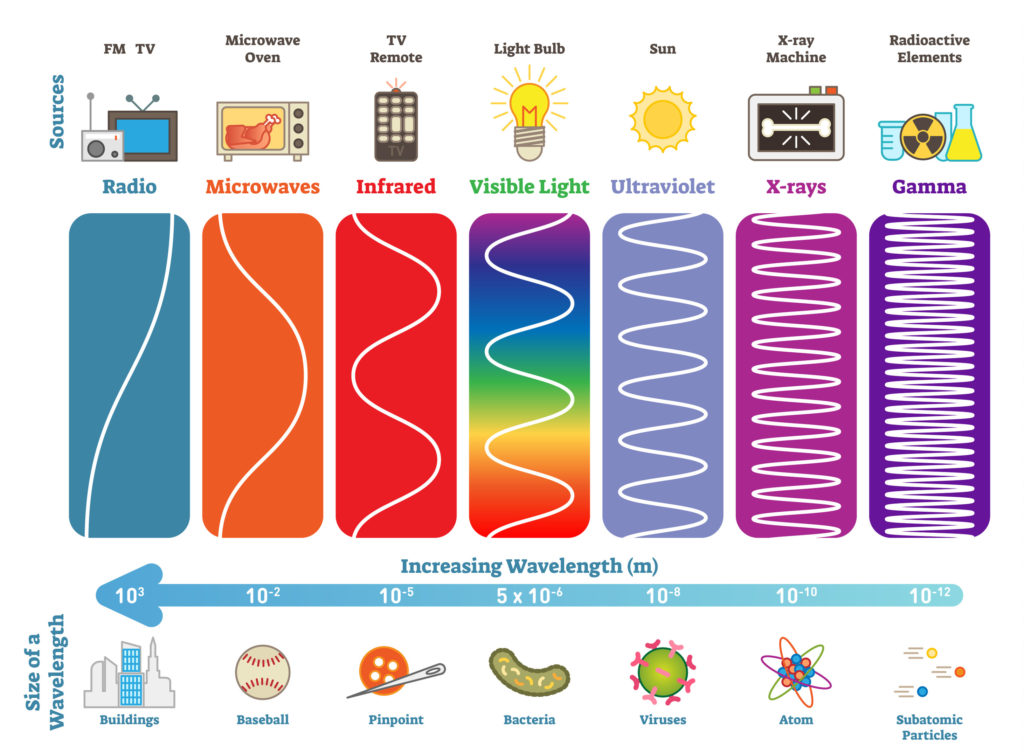
What’s the difference between frequency and wavelength?
Frequency is the number of waves that pass a point each second. Wavelength is the length of one wave.
The longer the wavelength the lower the frequency.
What is ionising radiation?
Ionising radiation can remove an electron from an atom or molecule. These atoms or molecules are then said to be ionised and are unstable.
Gamma Rays, X rays and some types of UV radiation are ionising.
Ionising radiation can lead to changes in the DNA of a cell.
Electromagnetic Spectrum Facts
We can only see visible light.
Different colours of visible light have different wavelenghts.
Gamma rays and x-rays pass through the body which make them ideal for medical imaging.
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves. They vibrate at 90 degrees to the direction the wave travels.
There are 7 different types of electromagnetic radiation but they merge together to form a spectrum.
The higher the frequency of the EM wave the more dangerous it is to humans.
Radio waves are not absorbed by the body.
Most of the UV radiation from the Sun is absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere, but some is absorbed by the skin where is can cause damage to cells on the surface.
All types of waves in the electromagnetic spectrum travel at the speed on light.

Last Updated on July 18, 2022 by Emma Vanstone

Leave a Reply