Mitosis is the stage of the cell cycle where the cell divides. Mitosis is used by multicellular organisms to grow or replace damaged cells. This paper plate mitosis activity uses pipe cleaners to show the stages of mitosis.
The key thing to remember about mitosis is that it produces two new daughter cells from one parent cell. Each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell.
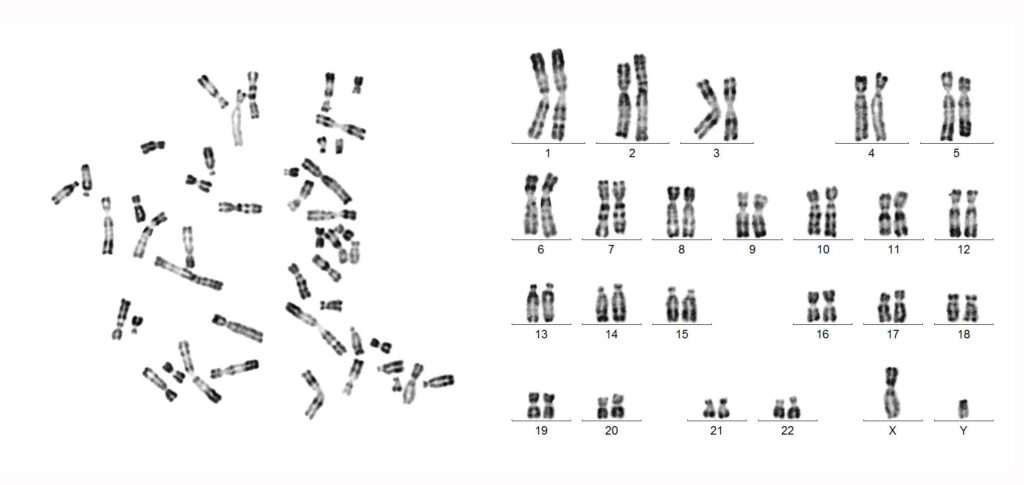
Mitosis is different to Meiosis where each new cell is not identical to the parent cell and only has half the number of chromosomes of a normal cell.
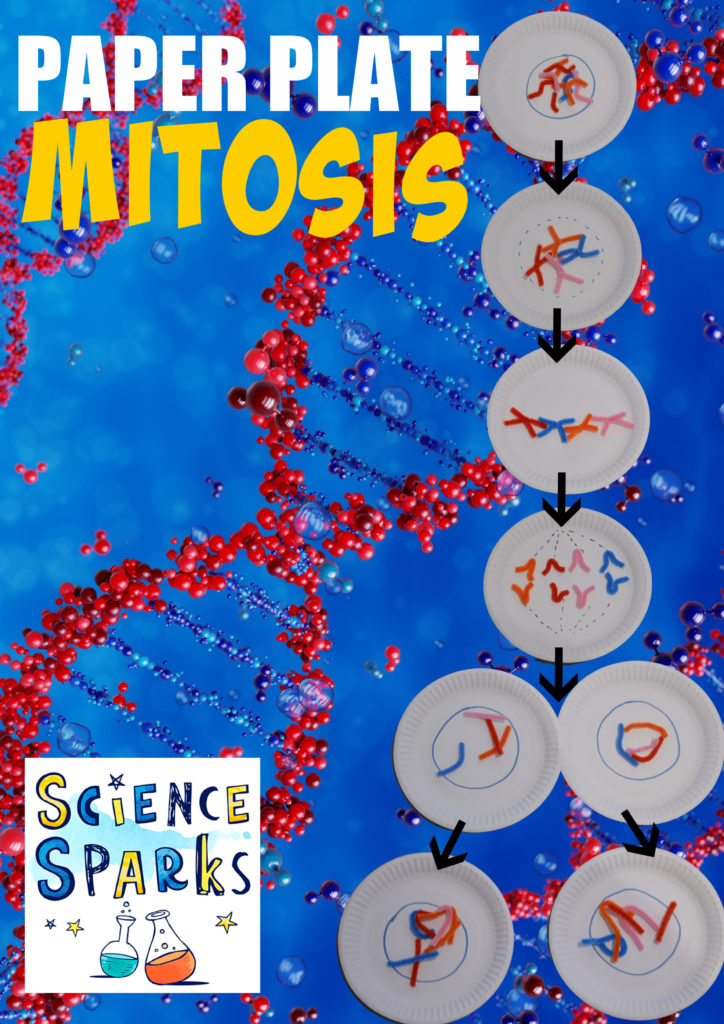
Paper Plate Mitosis
We used pipe cleaners and paper plates to demonstrate mitosis in a very basic way!
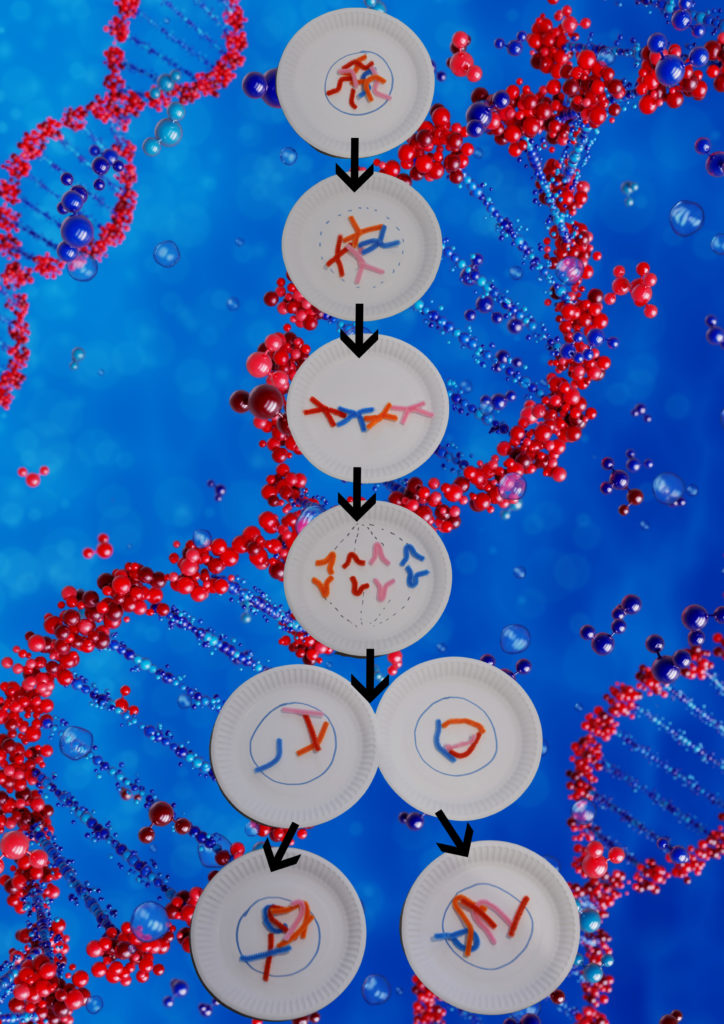
Interphase
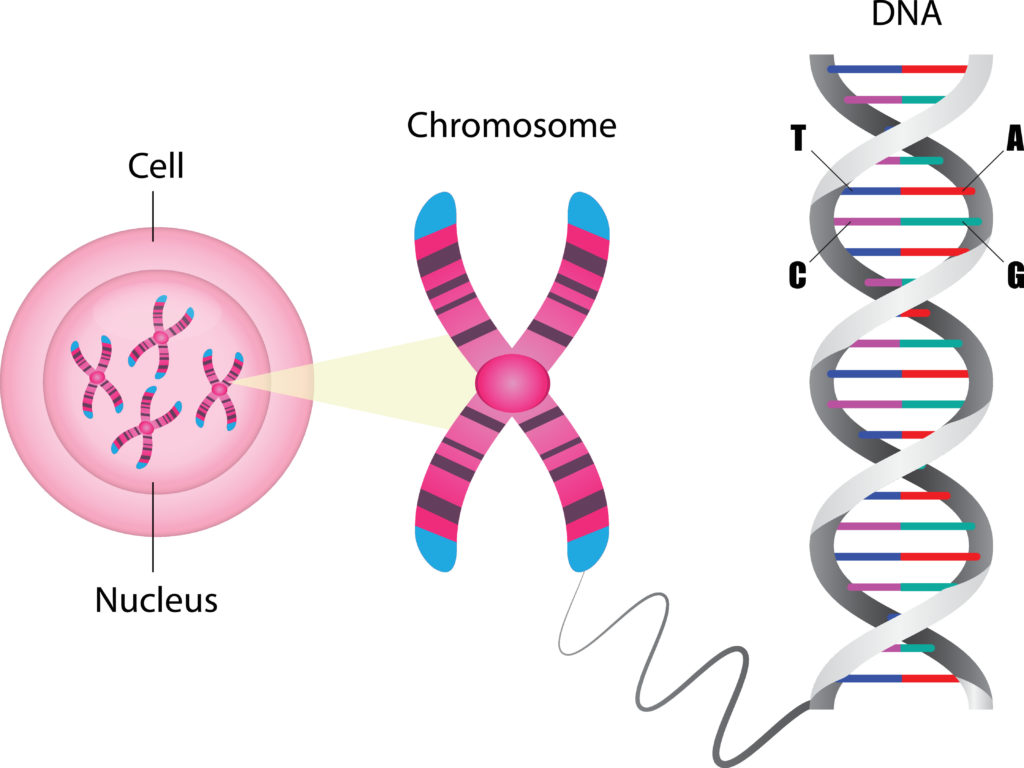
This is when a cell is getting ready to divide. It increases the number of subcellular structures ( mitochondria, ribosomes etc), duplicates its DNA and forms chromosomes.
A chromosome has two arms, the left has the same DNA as the right.
Each arm is called a chromatid.
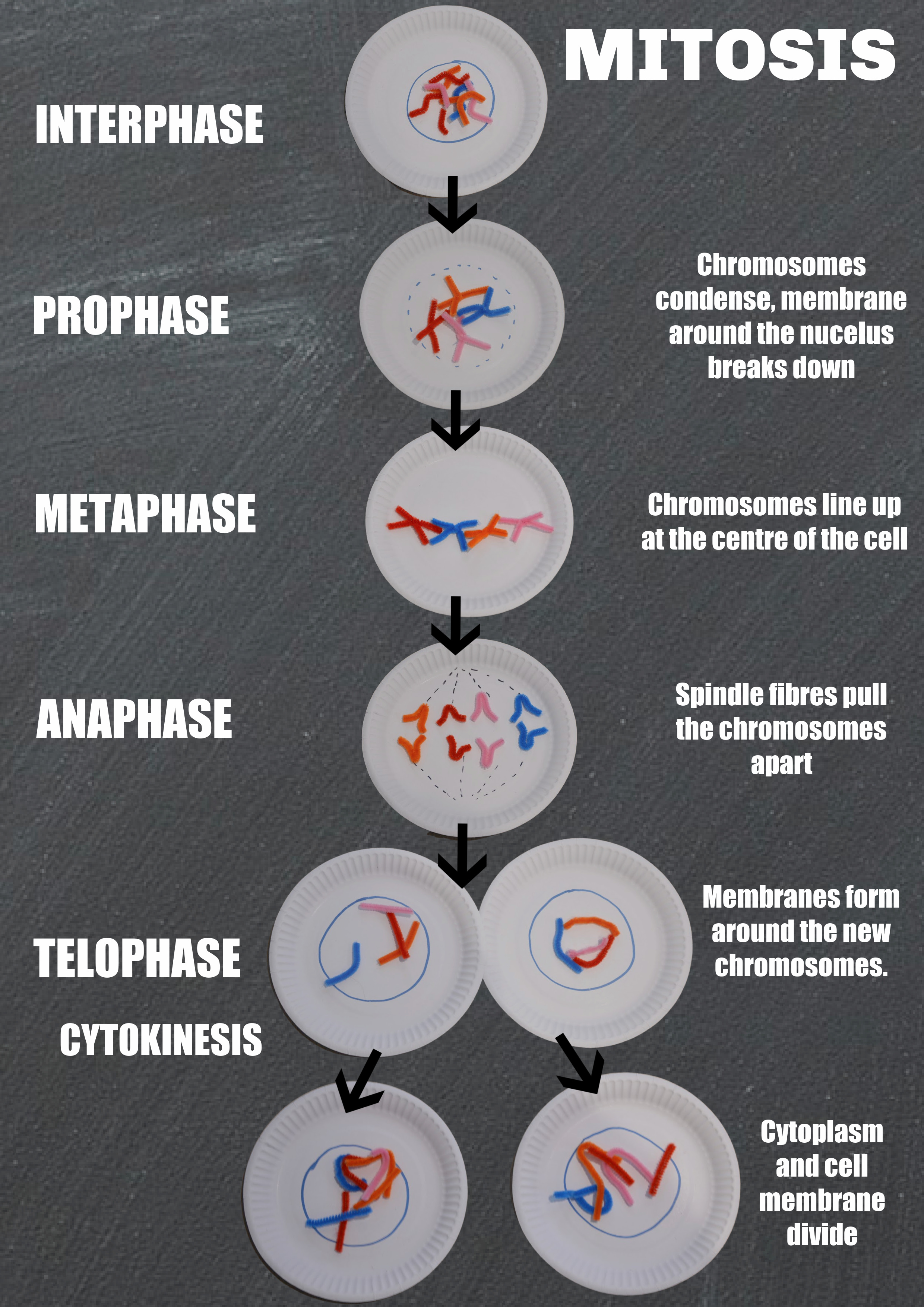
Mitosis
When a DNA has copied it’s contents and DNA it can go through the process of mitosis to divide.
Prophase
Chromosomes condense to become shorter, the membrane around the nucleus breaks down leaving the chromosomes free in the cytoplasm.
Metaphase
Chromsomes line up in the middle of the cell.
Anaphase
Spindle fibres form and pull the chromosomes apart. One chromatid from each chromosome moves to each end of the cell.
Telophase
Membranes form around each set of chromosomes. Each new cell now has it’s own nucleus.
Finally the cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to give two separate new cells. This is cytokinesis.
Mitosis – Quick Facts
Mitosis is where one cell divides into two genetically identical cells.
Mitosis occurs mostly for growth and replacement of damaged cells.
Mitosis is part of the cell cycle and usually divided into 5 stages.
More cell biology for kids
Find out about cell structure and function of subcellular structures with my cell models.
Create a DNA model using candy to learn about the double helix structure.
Last Updated on July 18, 2022 by Emma Vanstone




Leave a Reply