Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere which trap heat. An increase in greenhouse gases caused by human activity is responsible for the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Think how it feels when you enter a greenhouse or when you sit in a room with lots of windows on a hot day. It feels very hot. This is because sunlight passes through the windows creating heat which cannot escape. The same happens in our atmosphere. Sunlight passes through, bringing with it heat, which then cannot escape.

It's not greenhouse gases themselves that are bad, without them the Earth would be too cold for life to exist, but humans are adding too many greenhouse gases into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels and our general over consuming lifestyle. Even a small temperature increase could have a catastrophic effect on our planet.
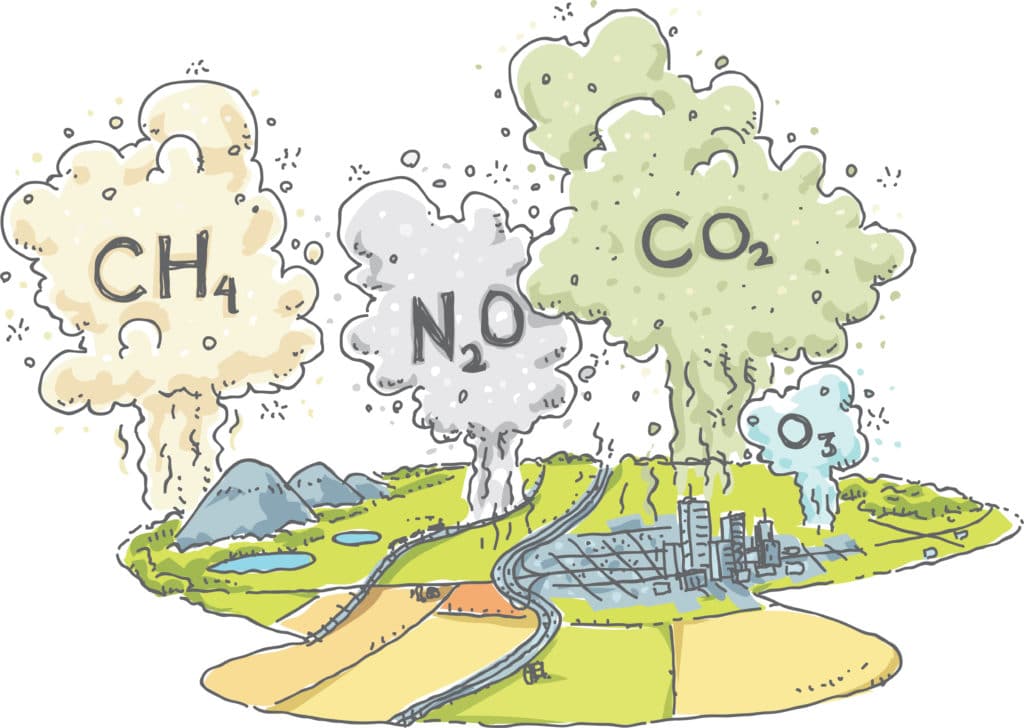
What are Greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases are mainly:
Water vapour
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Ozone
Nitrous Oxide
Chlorofluorocarbons
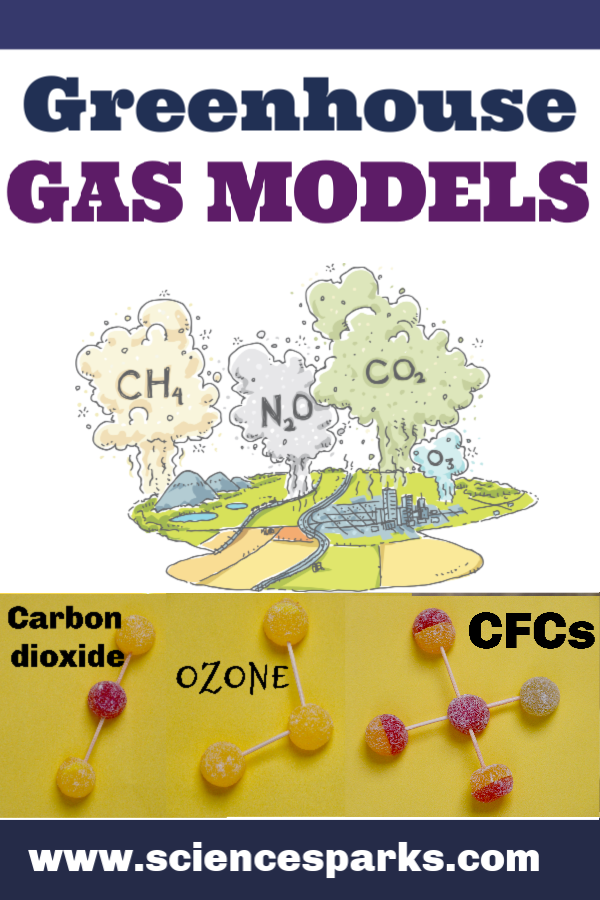
Greenhouse Gas Models
We modelled greenhouse gases using sweets, but balls of plasticine would also work well.
You'll need:
Toothpicks or cocktail sticks
Gummy sweets or plasticine ( lots of different colours )
Assign a colour to each of the following atoms.
C - Carbon
H - Hydrogen
Cl- Chlorine
O - Oxygen
Fl - Fluorine
Build your greenhouse gas models!
Methane Model
Methane is the gas often linked with cows. The chemical formula is CH4
This is 1 Carbon atom surrounded by 4 Hydrogen atoms.
Methane is released from livestock, landfill sites and when coal, oil and natural gas are extracted from the Earth.

Ozone Model
Ozone is a gas composed of three atoms of oxygen. It's blue and has a strong smell. The oxygen we breathe has two atoms of oxygen and has no colour or odour.
The ozone layer blocks radiation from the sun. Good ozone occurs naturally in the upper stratosphere ( the layer of space 6-30 miles above the surface of the earth ). It forms when UV light hits oxygen molecules, splitting them into two atoms of oxygen. If one O atom combines with an O2 molecule, ozone is created.

Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
CFCs are made up of chlorine, fluorine, and carbon.
If they contain hydrogen in place of one or more of the chlorine they are called hydrochlorofluorocarbons.
Chlorofluorocarbons are the greenhouse gas responsible for the depletion of our ozone later. They are man-made and not found in nature.
CFCs were found in aerosols, fridges and foam products. They break down ozone gas, which depletes the ozone layer, reducing its ability to protect us from the sun's harmful rays.
CFCs were banned from use in developed countries from the year 2000, but they are highly stable molecules that can last up to 100 years! There is some evidence that the ozone layer has started to repair itself thanks to the ban, which is great news and shows how fast and efficient action can make a difference.
The CFC molecule below contains 1 carbon atom in the centre, surrounded by 3 chlorine atoms and 1 fluorine atom.

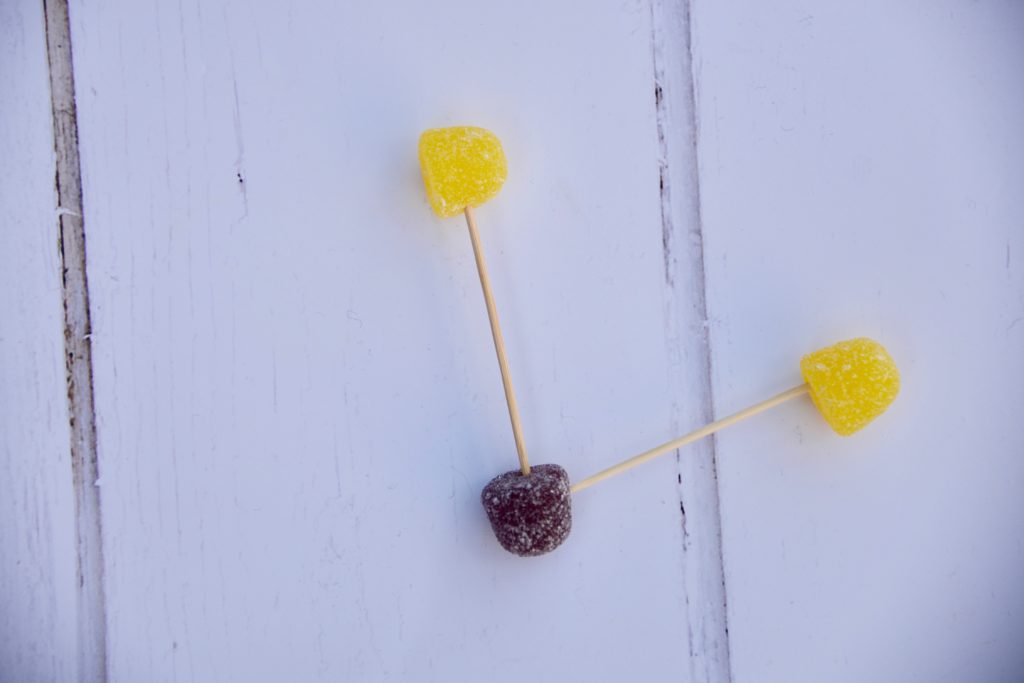
Nitrous Oxide Model
Nitrous oxide N2O is a natural part of the nitrogen cycle. Too much Nitrous Oxide ( from burning fossil fuels ) can lead to smog and acid rain.
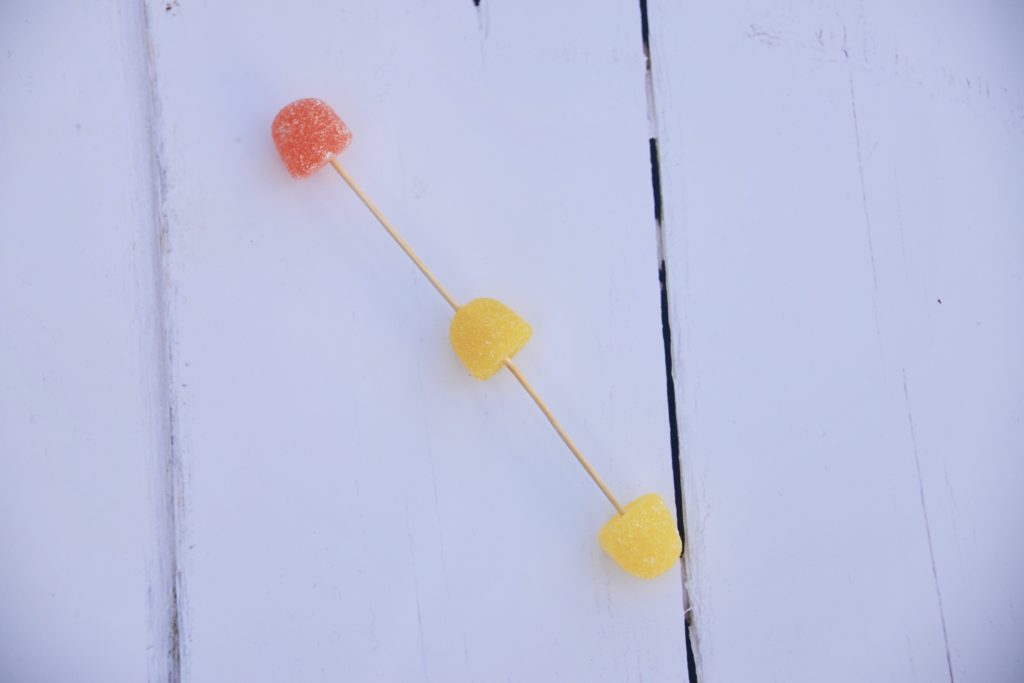

Water Vapour Model
Water vapour is water ( H2O ) in its gaseous form. It forms clouds and drops back to Earth as rain.
It might surprise you to know that water vapour is the largest contributor to the Earth's greenhouse effect, but this is directly related to the Earth's temperature. It's the increase in temperature that has led to an increase in water vapour in the atmosphere.

Carbon Dioxide Model
Carbon dioxide is probably the most famous of the greenhouse gases.
CO2 is released whenever fossil fuels are burned, carbon powered power plants and transportation are the main causes of the increase in CO2 we see.

How can we reduce global warming?
To slow down climate change we need to drastically reduce the amount of Carbon Dioxide ( and other greenhouse gases ) that we are pumping into the air.
How to reduce Carbon emissions
Use electric or hybrid cars.
Use heating and air conditioning less.
Recycle and reuse as much as possible.
Buy energy-efficient products such as light bulbs and unplug electrical devices when not using them.
Walk or cycle instead of taking the car.
Eat less meat, grow your own food and don't WASTE food!
Consume less generally.
Fight for renewable energy and for change!
Last Updated on February 10, 2024 by Emma Vanstone



Leave a Reply