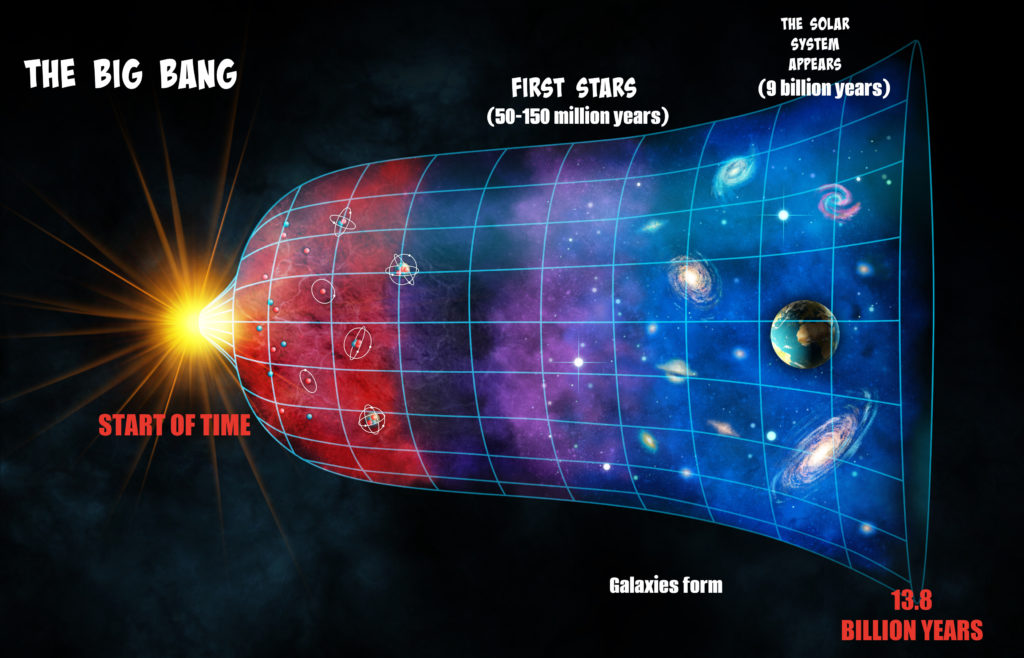
The question ‘How old is the universe?’ has intrigued astronomers for centuries. The discovery of leftover light from the big bang was not only supporting evidence for the big bang theory but also allowed scientists to calculate the age of the universe. The big bang is the current accepted theory of how the universe began and the start of time as we know it.
After the big bang the universe expanded very quickly. As it expanded it cooled. Remember energy cannot be created or destroyed, so all the energy in the universe today was around at the time of the big bang!
As the universe expanded the energy became stretched out over a bigger area and so the universe cooled and became less bright.
The first atoms formed about 380,000 years after the big bang when electrons and protons joined together. Photons ( another really small particle ) cooled and stretched to form cosmic microwave background radiation or CMB radiation. It is this radiation that scientists measure to learn about the beginning of the universe.
By estimating how far light from CMB radiation has travelled to reach Earth, the age of the universe can be calculated.
Scientists agree that the Universe is about 13.8 BILLION YEARS OLD.
Learn more about the universe
Learn more about the universe with Chromoscope. Chromoscope lets you explore the Universe in a range of wavelengths!
Help scientists search for new worlds by joining The Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 citizen science project.
Make a simple model of how the universe is expanding.
Science Concepts
- The Big Bang
- Atoms and subatomic particles
- Electromagnetic radiation

Last Updated on July 16, 2022 by Emma Vanstone

Leave a Reply