When part of a liquid or gas is heated, it expands and becomes less dense. The warmer, less dense liquid rises upwards, and the cooler liquid falls to take its place. This cycle of a liquid or gas rising and falling is called a convection current.
We set up a very simple convection current demonstration using hot and cold water with food colouring to show the movement of warm water through cold water.
Convection Current Demonstration
You’ll need
Tall glass or vase
A smaller glass or cup
Hot water
Cold water
Food colouring

Instructions
Fill the tall glass or jar with cold water.
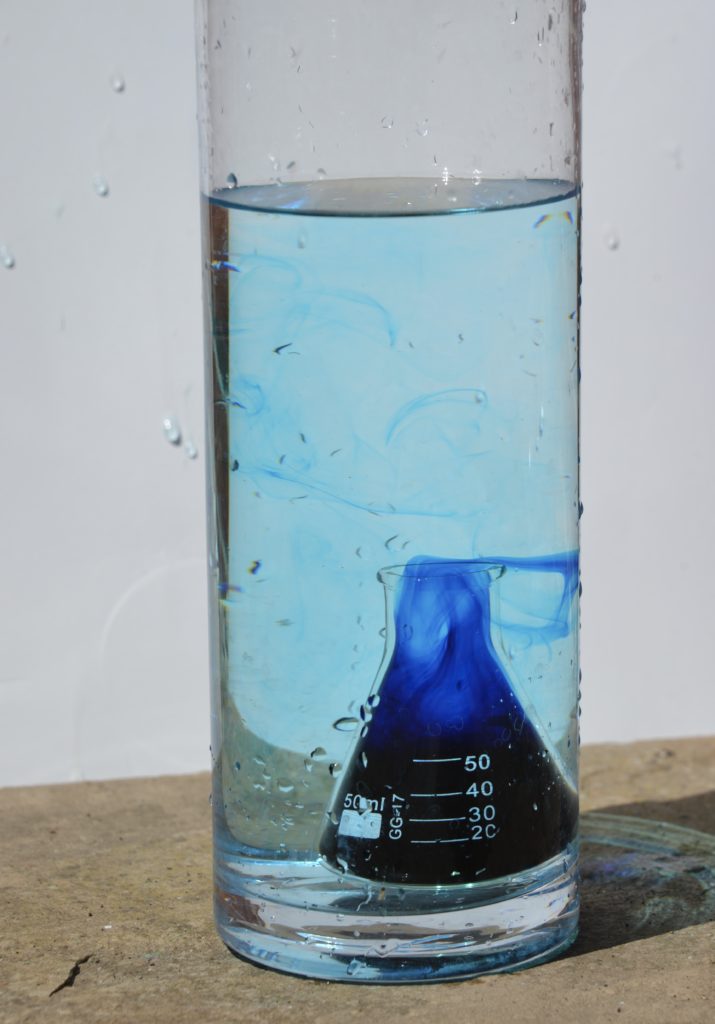
Fill the smaller container with hot ( but not boiling water ) and add a few drops of food colouring.
Carefully place the small container into the container with the cold water.
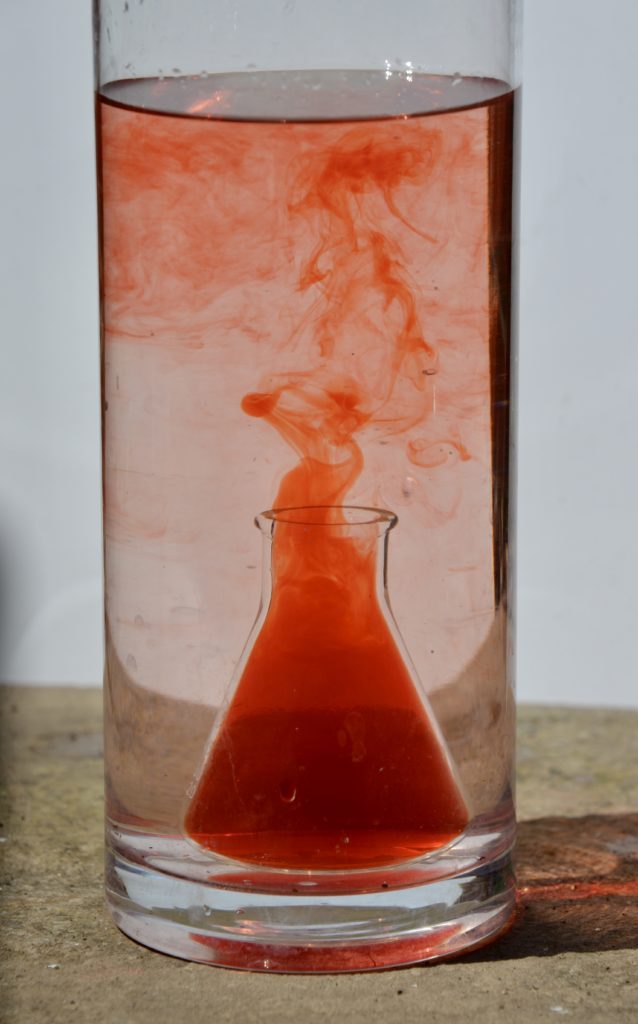
Watch what happens to the warmer, coloured water.
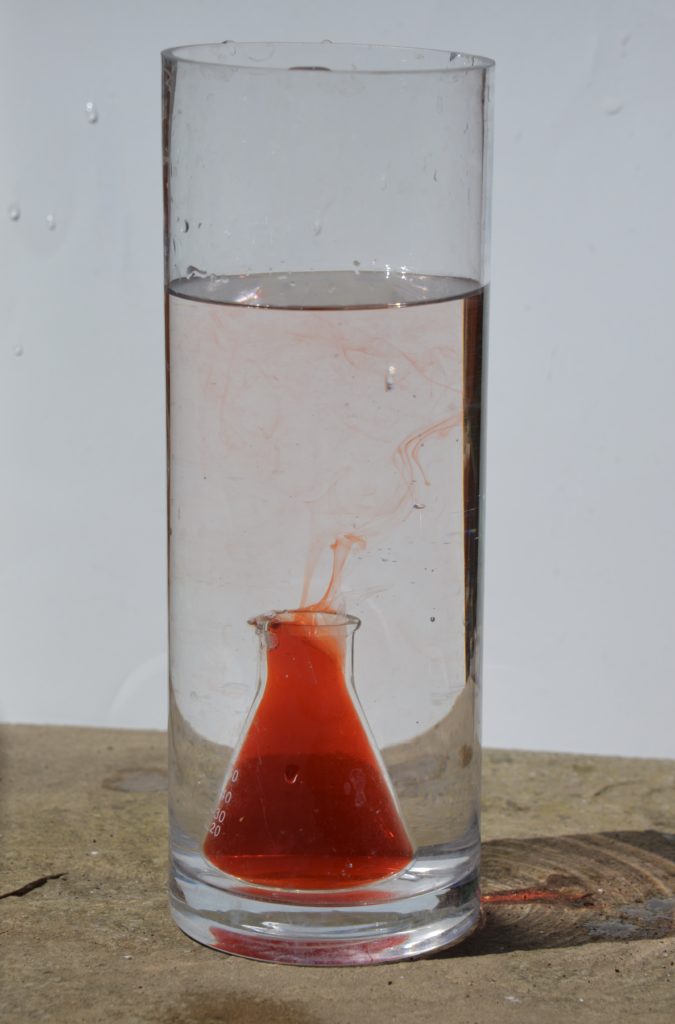
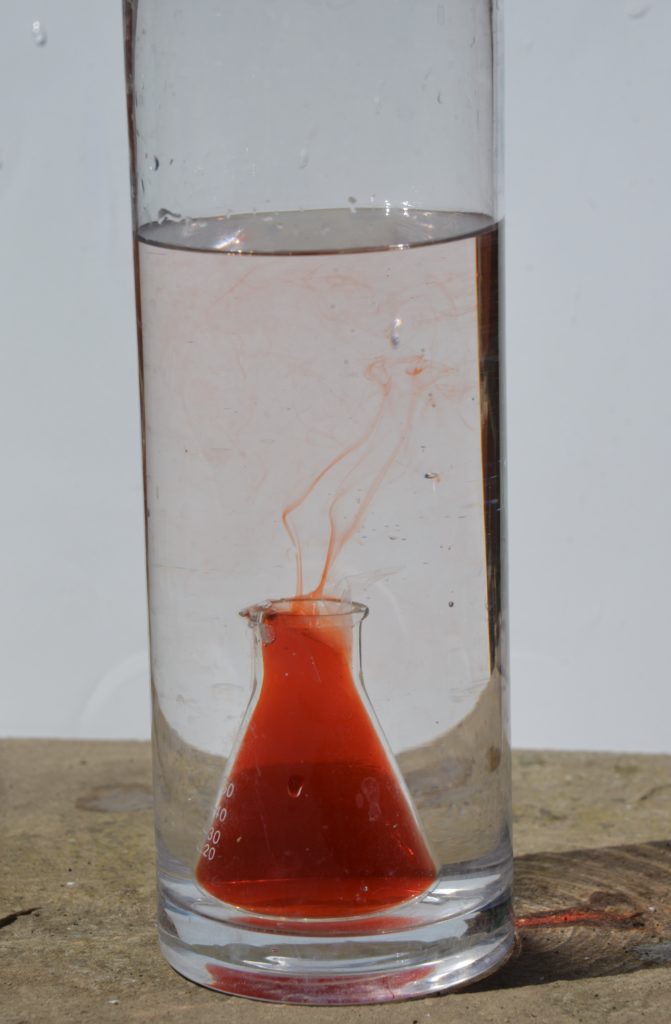
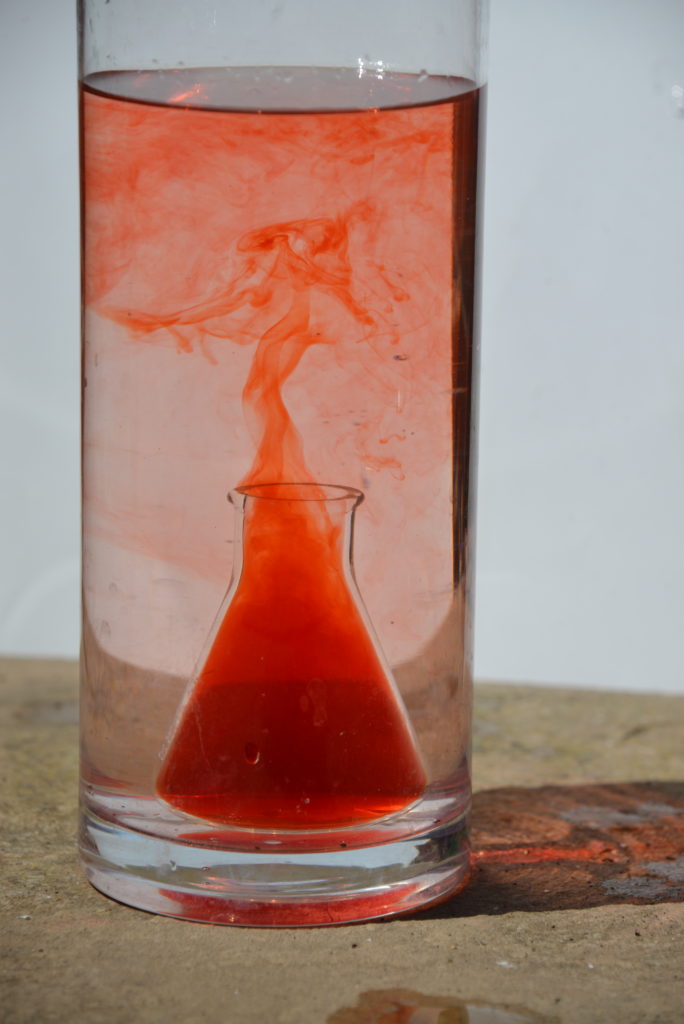



The hot, coloured water rises upwards and collects at the top of the cold water. It then cools and sinks downwards. Eventually, all the water will be at the same temperature.
How does convection work?
Particles of warm water move more quickly and spread out. They rise upwards through denser, cooler water, which sinks to the bottom, where it warms up. Eventually, all the liquid is at the same temperature.
Warm water rises because when liquids and gases are heated, they expand. This means they take up more room but have the same mass, so their density is less than when they are cool. Substances with lower densities float on substances with higher densities.

A hot air balloon is another example of convection currents in action.
Ask an adult to help with this activity
Extra Challenge
Repeat the activity with cold water instead of hot and watch what happens to the coloured water.

You can see that the cold water isn’t moving upwards like the warm water.
How is heat transferred?
Heat can be transferred in three different ways.
- Conduction.
- Convection
- Radiation.
Convection
Heat convection occurs when warmer molecules of a liquid or gas move from a warmer to a cooler area, taking the heat with them.
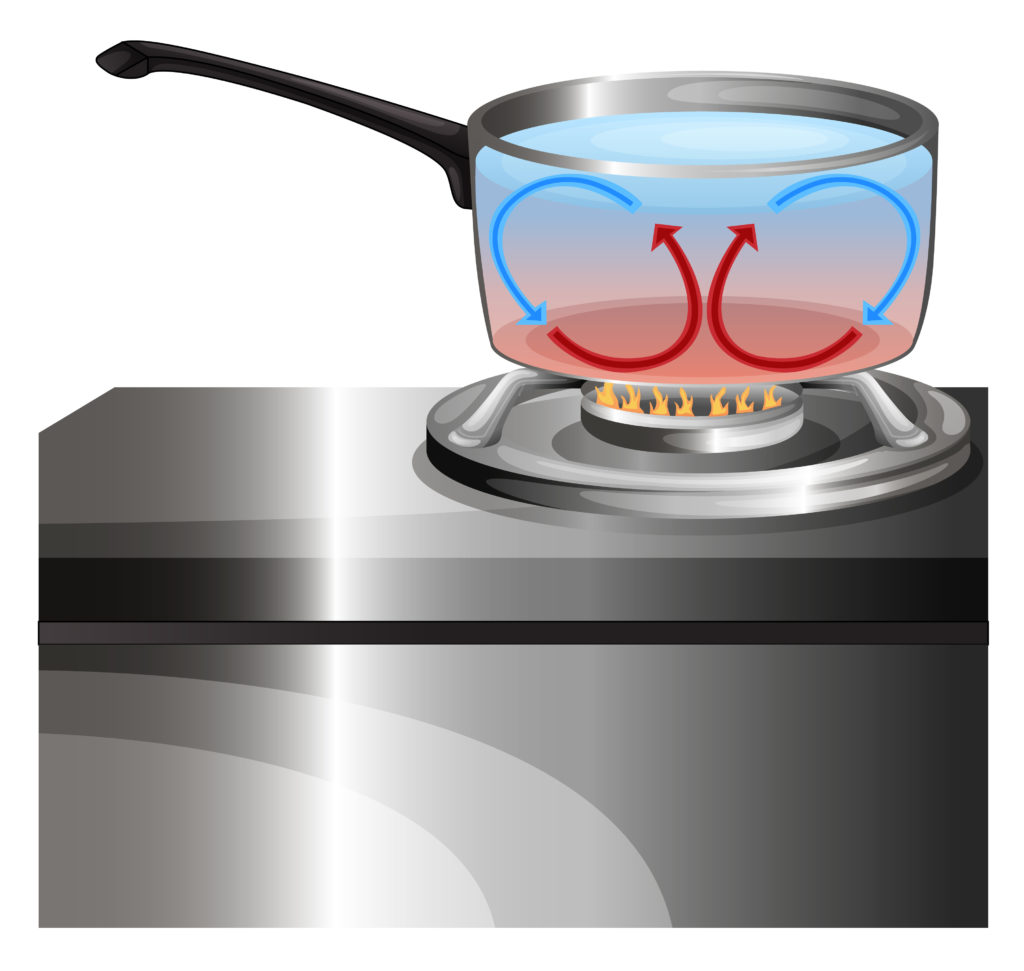
Water being heated in a pan is an example of convection. This is the type of heat transfer we demonstrated above.
Another way to demonstrate convection is with a spinning convection snake.
Conduction
Conduction of heat occurs when vibrating particles pass any extra vibrational energy to nearby particles. The more energy the particles have, the hotter the object gets. An example of this type of heat transfer is when metal pans are heated on a hob. Heat travels through the pan. If the pan handle is also metal, it will get hot, too. This is why metal pans often have plastic or wooden coverings on their handles. Plastic and wood are not good conductors of heat.
Radiation
Radiation of heat is when heat is radiated to the surrounding area by heat waves. Particles are not involved in this kind of heat transfer.
The heat from the sun travelling through space is an example of heat transfer by radiation. Waves transfer this type of heat.
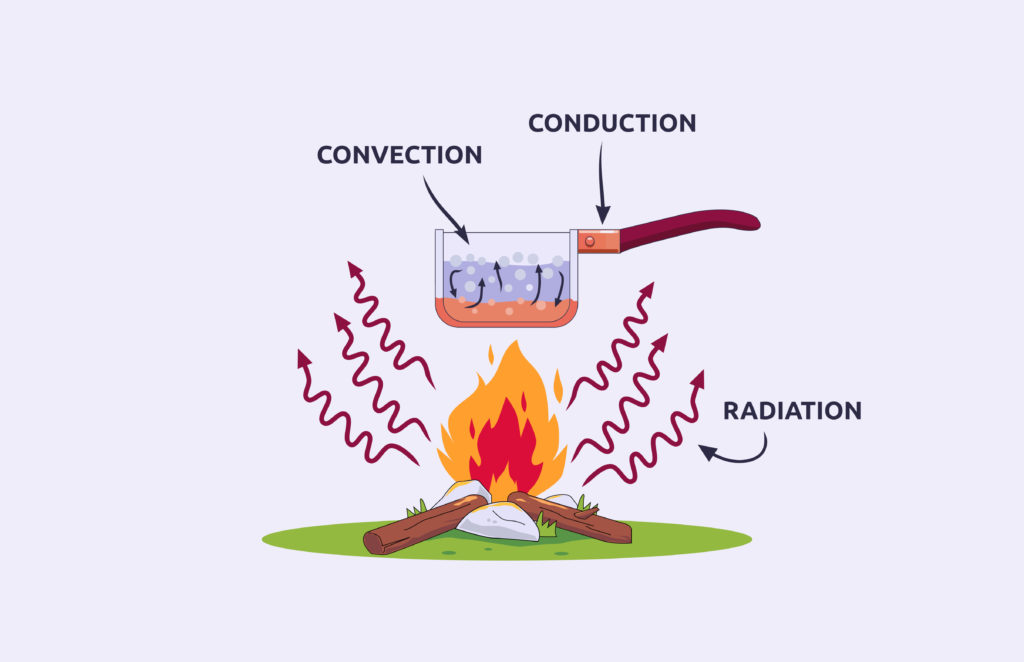
The campfire and pan example above shows all three kinds of heat transfer.
Heat travels by radiation from the campfire to the metal pan. Heat travels through the pan’s metal by conduction to warm the lower layers of water. The water is then heated by convection as the less dense warmer water rises through the cooler water, creating a convection current!
Remember – heat is only transferred if there is a temperature difference.
Science concepts
- Density
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
- Heat transfer

Last Updated on August 25, 2024 by Emma Vanstone

Leave a Reply